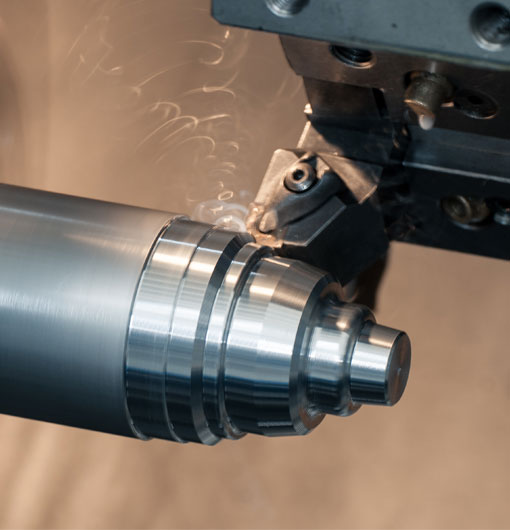
In the vast horizon of innovation, where the marriage of technology and traditional techniques spark new possibilities, CNC turning has found a significant place in the ceramics industry. If you believed ceramic materials only hold relevance in pottery or sculpture domain, prepare to have your perceptions reimolded. This article promises an enlightening expedition into the fascinating world of ceramic CNC turning.
The Fusion of Ceramics and CNC
Firstly, let's unravel the concept of CNC turning. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) specifically refers to a process utilized in the manufacturing industry that involves the use of computers to control machine tools. It has been adopted in varying sectors, now including ceramics, symbolizing an exciting convergence of time-honored artistry and cutting-edge technology.
Ceramics being naturally brittle and sensitive to stresses, demand precision and careful handling. Utilizing CNC machines for their modeling ensures accuracy to micrometers and minimal error probability. This efficiency leads to streamlined operations, decreasing waste and increasing productivity, all while maintaining absolute precision.
A New Dawn in Manufacturing Industry
CNC turning machines in ceramics manufacturing employ both traditional turning methods and innovative techniques. Metals and plastics have long been shaped and re-shaped by these machines, but ceramics offer a unique challenge and equally distinct potential.
The ceramics processed by CNC extend to silicon nitride, alumina, zirconia, and more. These materials possess great strength and hardness, endurance to wear, heat and corrosion, electrical insulation, and low density. Such traits infer their application in multiplicity of fields like electronics, medical, severe environment conditions, etc.
How Ceramic CNC Turning Operates
Before proceeding to milling or turning ceramics, it's crucial to study their composition, hardness, flexibility and strength. Implementing ceramics in a CNC environment includes sintering, a high-temperature process hardening the ceramic without melting it, thus making it machinable.
Understanding the CNC process, the initial phase involves designing the desired component on a CAD software. This digital model is then converted into a CNC program, feeding the machine with positional data for tooling actions. Subsequently, the selected ceramic block is loaded into the CNC machine and the automated process begins, carving out the prospective design with the utmost accuracy.
Practical Applications Galore
Ceramic materials worked upon by CNC turning machines find usage in countless applications. Electronic industries employ ceramics due to their insulating properties. In medical arenas, the bio-inert nature of ceramics grants scope in hip joint replacements or dental crowns. Their heat-resistant nature caters to their utility in furnace components, welding pins, etc.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Ceramic machining does pose certain challenges - ceramics are hard and brittle, milling them requires high feed rates and lots of coolant. Moreover, the cutters need to be frequently replaced, and the ceramic dust poses a disposal problem.
Nonetheless, the vast potential of this technology cannot be undermined. Use of diamond tools and innovation in machining process are bound to decrease the challenges, opening promising prospects for the future.
In conclusion, the advent of ceramic CNC turning marks a new era, transforming the manufacturing landscape. As we embrace this technological symbiosis, new pathways for design and development unfurl. Let's anticipate a future replete with more advances and applications of this remarkable technology.
ceramic cnc turning